
Thermoset vs Thermoplastic: Full Comparison

Thermoplastic vs Thermoset: what are the differences and which one should you choose for your application?Thermoplastics and thermosetting sound very similar, they are both polymers, but they have various properties and different production methods.
Complete this article to know the answers for these questions:
- What is the main differences between the thermoplastics and the thermosetting?
- Are thermoplastics & thermosetting recyclable?
- What about the injection molded process for thermoplastics and thermosetting?
- How to manufacture thermosetting & thermoplastics?
- Can thermoplastics & Thermosetting be repaired?
- How thermoplastics and thermosetting can be used in daily life?
- What are the pros & cons for thermosetting plastics?
- What are the pros & cons for thermoplastics?
- Which are stronger thermoplastics or thermosetting plastics?
- What are the examples for thermoplastics & thermosetting
1. Thermoplastic VS Thermoset
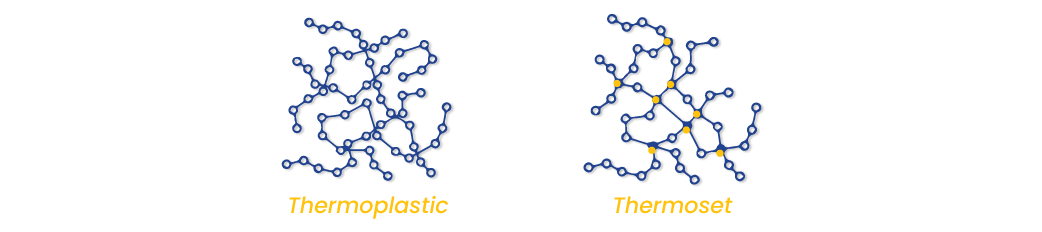
What are the main differences between the two polymers?
Polymers is divided into Thermoplastic & Thermosetting. Here are the 5 Main differences between them:
- Synthesizing
Thermoplastics depend on “addition polymerization process”.
Thermosetting depend on “condensation polymerization process”.
- Processing
Thermoplastic can be processed by injection & rotational & blow molding and extrusion process.
Thermosetting Plastic can be processed by reaction injection & compression molding.
- Bonds shape
Thermoplastics bonds are secondary between molecular chains.
Thermosetting plastics are primary between molecular chains.
- Melting point
Thermoplastics have low tensile strength and low melting points.
Thermosetting plastics have high tensile strength and high melting points.
- Molecular Weight
Thermoplastic is lower in molecular weight than Thermosetting plastics
Now after you know the main differences between them, it’s time to answer the most important questions about these plastic types.
2. How to manufacture thermosetting & thermoplastics?
Thermosetting Manufacturing
Thermosetting production process depends on the liquid molding processes. The manufactures fed the polymers and the other agents into tanks and barrels then they heat and mix them.
Then they put them into a mold cavity. Then the material goes to curing process that prevents the risk of the material melting. The final step is subjecting the final product to high heat that make the thermoset plastics suitable for high-heat applications.
Thermoplastics Manufacturing
Injection molding is the main method to manufacture thermoplastics. There are many standard processes that you can use many to produce thermoplastics such as extrusion, molding, grinding, and welding. Plastic Injection molding still the most effective way to manufacture high quality thermoplastics for both low and high-volume production.
3. What about the injection molded process for thermoplastics and thermosetting?
Thermoplastic parts are used widely for consumer plastics such as the plastic that used in milk bottles, let’s see which better for plastic injection molding:
Thermoplastic polymers can be easily melted, and it is easy also to inject it to a mold to create new part. Then you can wait until this part cooled then you can open the mold to eject the part.
In thermosetting injection molding, to create a new part you have to inject the cold material into very hot mold, but it will be so difficult to melt this part again.
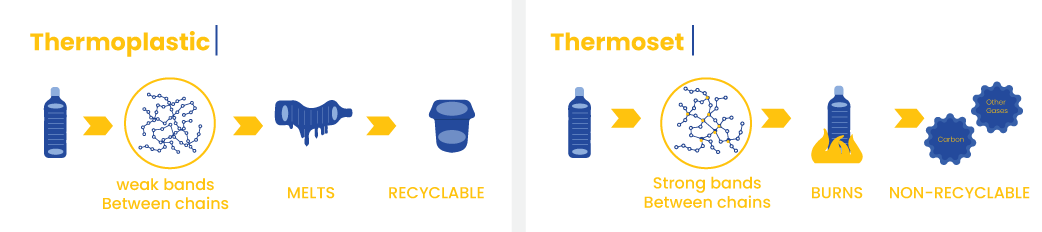
4. Are thermoplastics & thermosetting recyclable?
In accordance with its properties, thermoplastics bonds are secondary between its molecular chains so you can easily heat and remold it for manufacturing new shape or new design.
Thermoplastic materials are highly recyclable as it can be shaped easily to any form.
Unlike thermosetting which cannot be recycled because of its structure as they have cross-link structure, and they have high tensile strength.
5. Can thermoplastics & Thermosetting be repaired?
Thermoplastics cracks can be repaired easily while repairing thermosetting cracks are difficult. Thermoplastics are comprised of elastic amorphous regions in its solid state while thermosetting are reinforcing fiber in the same state.
6. How thermoplastics and thermosetting can be used in daily life?
Thermoplastic polymers are widely used to manufacture wide range of applications such as carpets, piping systems, car batteries, gas filters and ropes.
Now let’s know thermosetting polymers applications, you can find thermosets in electrical components, heat shields, motor components and insulators.
7. What are the pros & cons for thermosetting plastics?
Thermosetting have a lot of advantages such as heat resistance. They have good electrical insulation properties. It has corrosion resistance and good dimensional stability. They are also cost saving as their tools are cheaper than thermoplastics and they need cheaper setup. They are also available in a wide range of surface finishes and colors.
When it comes to thermosetting cons, as we mentioned they cannot be recycled or remolded.
8. What are the pros & cons for thermoplastics?
Let’s start by thermoplastics pros, they are resistant to detergents and chemicals. They have good electrical insulation. They have high impact and corrosion resistance. Thermoplastics can be reshaped and recycled.
Thermoplastics has few cons such as they are more expensive than thermosetting polymers and they are not suitable for all applications as they get softer when exposed to heat.
9. Which are stronger thermoplastics or thermosetting plastics?
Thermoset plastics generally have high strength and offer dimensional stability. It doesn't soften because of its strong crosslinks. While thermoplastics are soften by heating.
10. What are the examples for thermoplastics & thermosetting?
Thermoplastics
Thermoplastics represent ay plastic material that turns into soft form at a specific temperature and then becomes solid upon cooling.
They are many examples for thermoplastics such as polyester, Polypropylene (PP), Polystyrene (PS), Teflon and acrylic.
Thermosetting
Thermosetting plastics can be stored in liquid form. thermosetting include polyurethane (PU), EPOXY, silicone and phenolic. Every material offers unique advantages. For instance, phenolic has flame resistance while epoxies are chemical resistant, tough and elastic.
Suggested Blogs

Exclusive vs. Non-exclusive Distributor
GAP Polymers Team
Have you ever wanted to know the difference between the exclusive and the non-exclusive polymer distributers, GAP polymers will help you to know the main differences between them.

An Overview of Polypropylene Thermoforming Process
GAP Polymers Team
PP is the second most popular plastic resin in the world used across many industries. Thermoforming PP has become a process of choice for many manufactures due to its versatility low cost , and more.

Weekly Plastic News & Resins Pricing
GAP Polymers Team
A weekly coverage of all you need to know about the international plastic industry including resin pricing, trends, market insights, and more.

A Deeper Look Into Plastic Manufacturing Industry
GAP Polymers Team
Keep up with the rapid changes of the plastic manufacturing industry and dive deep into what shapes the polymer industry and how to choose the best raw material supplier for your business.

Polymer Industry Updates: What's coming up in 2023?
GAP Polymers Team
2023 is a critical year in the polymer industry at all levels. Global polymers market size is expected to grow finally after the economic recovery from the pandemic.

Top Plastic Raw Material Suppliers
GAP Polymers Team
The polymer industry is facing continues challenges and choosing the best supplier is getting harder. Look no further and explore the full list of the top plastic raw material suppliers.